The first hominids ( AUSTRALOPITHECUS ) appeared in central Africa, they lived in the equatorial zone with a warm climate. Did not need shelter and did not know fire.
PALAEOLITHIC PERIOD
-Moved to the north ( HOMO ERECTUS ) nd we know about them with the settlers in Atapuerca or Terra Amata. Terra Amata had spring camp for a group of hunters, named like the beginnings of the architecture.
Characteristics:
- Walls of branches
- Huts surrounded by aligned stones
- Interior posts supporting the central beam
- Central fireplace, suggest a congregation
-(HOMO NEANDERTHALENSIS) They inhabits caverns in North Africa, Europe and the East.
Caverns : In Iraq, graves surrounded by flowers and branches, alignments to movement of the sun, have been discovered. This shows that there is a belief about the continuity of life after death and complez social structure.
-(HOMO SAPIENS) Great intellectual capacity is manifested in the sculptures and cave paintings found in caves and shelters.His successor is the modern man (Homo sapiens sapiens).
Eastern Europe Huts, dwellings are located in Eastern Europe, huts of circular plant and domed form with frame that was covered possibly with skins of animals.
In Ukraine, near the Dniester River, there are remains of huts from 44,000 and 12,000 years ago,reinforced with bones and skulls of mammoths. These dwellings must have housed large family groups, reaching very large diameters (some up to 9 m).
NEOLITHIC PERIOD
Agriculture was alredy firmly established and sedentary lifestyle encouraged the construction of permanent housing. Social organization became more comlex and different types of buildings appeared. The first great Neolithic city is Çatal Huyuk according to some historicians
Çatal Huyuk in Turkey it was not an exclusively agricultural community but a vital node in commercial network, transport of minerals…etc.It was sep up as large rectangular buildings clustered together and without streets. House had two floors, builded with pressed adobe bricks and wooden roofs and no front door.

MESOPOTAMIA
There were large cities that were peranetly inhabited in the valley between the rivers Tigris and Euphates ( Mesopotamia ) present-day Iraq. Writing developed and so domestic pottery. The urban architecture was made with adobe or brick.
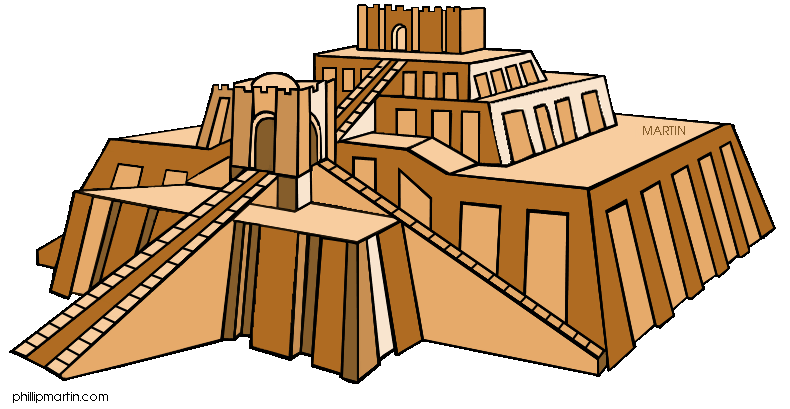
Ziggurats is a type of massive structure built in ancient Mesopotamia. It has the form of a terraced compound of successively receding storeys or levels. They had a core of raw, sun-dried adobe of brick and a covering of fired brick taken wich a thick mortar of bitaminous material that gave high resistance.
They are temples built on top of natural or artificial patforms, overlapped and stepped with ramps and ascending stairs, imitanting the dwellings of the gods.
The oldest temple of this type was built in Uruk towards the end of the fourth millennium, but it was a new king of Ur, Ur-Nammu.
he structure resembles the pyramids of Egypt, but are more similar to the pyramid of Central America built much later.
EGYPT
It is necessary to consider the Nile river. Life was peaceful and o hight quality following the cycles of eater and the sun. The organization of the temples and cities follow the two perpendicular axes: the river and the sun.
City of Lahum the area was divided in the acropolis, it has lots of big paleces and middle residences.
- Temple is the most important public building, place o veneration and center of learning and training for the administration of the country. It was the house of the gods. It represents the architecture of permanence and immutability and it symbol of durability was solidity.
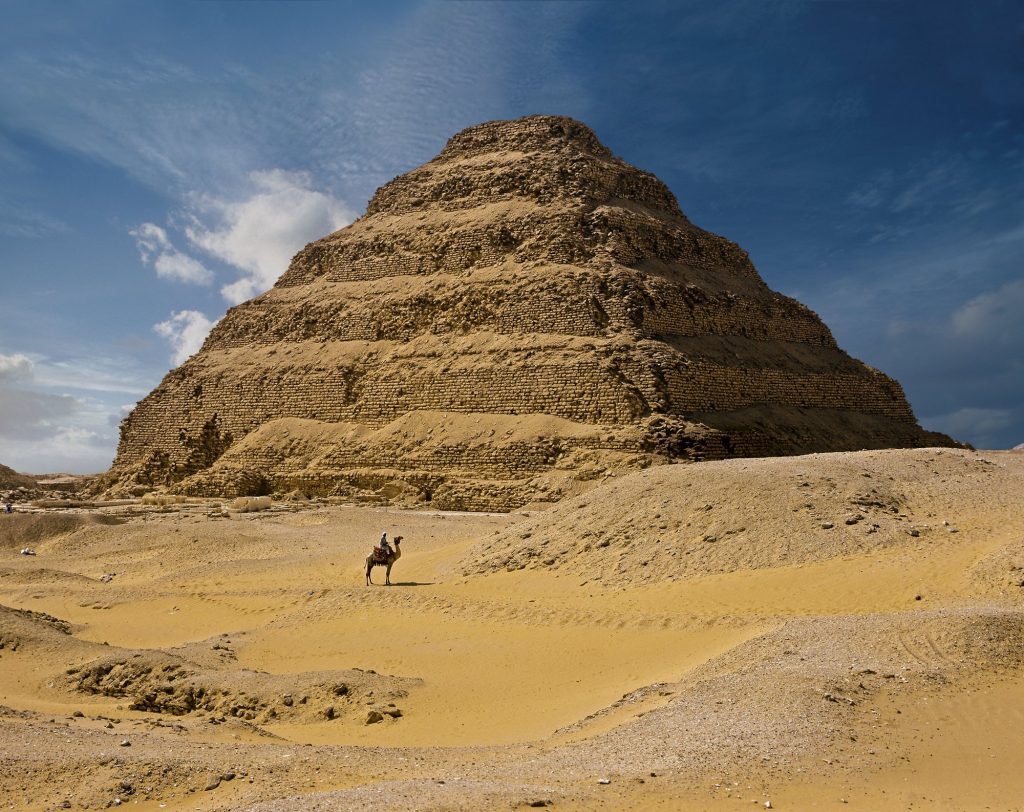
- Pyramids hence the cult of dead reflected in the pyramids, eternal constructions. The architect Imhotep changes funerary architecture by inventing the stepped stone pyrimid for Zoser. He transforms the mastaba into a stepped pyramid, bringing the concept of elevation and replaces adobe brick and tree trunks with limestone masonry.

limestone masonry

ANCIENT GREECE
They learned from Egyptian architecture and sculpture, but also creating their own style based on the exaltation of human capabilities. Greek architecture expresses the search for equilibrium between vertical and horizontal load-bearing elements. Each element was very worked with the best materials as the best method of satisfying the gods and homoring the polis. The aim was to achieve the excellence, in aim, detail and execution.
The ancient Greek vision of aesthetics and simplicity, clean lines, proportions, perspective and the search for harmony would continue to influence the architects of Rome and later dominate the Renaissance.

The polis. Greek cities grew up around fortiications with high ground named acropolis. Greek polis incuded the city and the surrounding farms . It is a grid-based plot in wich tge buildings are organized in zones and related functirones, based on the orographic situation and landscaped. The main streets included de agora, the center of greek community life, first configured by private houses and shops, and then to stoas.
Religious buildings: TEMPLE.
It was the most important building, dedicated to divinity. It was placed on a base or stepped platform ( stylobate ). Inside the nucleus was the cella, a very simple closed space, where the divine image was kept. The initial base as form o wood. The interior was not accesible to the public and it contiened large sculptures. The façade deserved maximum artistic attention (the public rites were celebrated in the altar in front of the temple). Great technical perfection was reached, as optical resources, to avoid visual deformations and to achieve harmony.

• The Parthenon, dedicated to the goddess Athena, is a Doric temple, octastyle and peripteral (the columns surrounding the whole building, being 17 on each of the major sides.
Theatre and Stadium. The largest open-air buildings. stadium for entertainment and sport events. Theatres located on the slopes of a hill. The stage You could see the polis. Harmonious proportions and excellent acoustics and grate capacity.
Houses. The greek architectures was that of the sculptural volumes organised in balance contrast with the landscape. Greek houses were simple. They had a central courtyard or peristyle, a construction tradition from the Roman architecture.
ROMANS.
The settlement of the Latins in the center of the Italian peninsula occurs around 1,100 BCE. Romulus and Remus founded the city of Rome.
Roman architecture was universal, embodying the essence of the romanitas wherever it was built. With the discover of concrete, created new forms and experimenting interior space, light and shadows. The most singular advance was the spaces with arches, vaults or domes. Stability, functionality and magnificence.
Temple. They used the greek orders with a certain liberty. Released to naturalism, vitality and energy of the Etruscans. They added two orders; Tuscan and Composite. They placed the temple with a high podium in the axes of the door of the cella. The usually were pseudoperiptera
Other types of plants ( circular, cruciform ) They used elements such like arch and vault. The Pantheon of Rome, is the one that best represents the achievements of Rome. Temple dedicated to all gods, including the deified Emperor Augustus.
Civil works. They were specialists in the design such as, Sewage networks, aqueducts, roads, bridges and walls. The romans also designed commemorative buildings such as, Triumphal Arches and Commemorative columns.
Commemorative buildings
Triumphal Arches: ceremonial works and a source of architectural and sculptural details.
The arch of Constantine is a rectangular structure with three openings, one central and the other auxiliary. There are columns on pedestals that rise up to an entablature. Above it is a super structure called an attic, with signs and reliefs.
Commemorative columns: monuments erected to commemorate an important event, such as a military victory. The Trajan’s column commemorates the victory of Trajan against Dacians.
Thermal baths. The romans played an important social role. The biggest served as baths, a place to exercise the body, a library, a school, a place for commercial relations, sculptures….
Theatre. Romans theatres derive form the Greek model butare i greater proportions. Their steppes werw built on a radial system of inclined concrete vaults raised on stone pillars. they were semi.circular and not horseshoe like the greeks. Function was for Rome and Greek plays.
The main parts of a theatre were:
- Scænæ: stage house.
- Orchestra: space between the cavea and the scænæ.
- Cavea: seating section.
Amphitheater. The main Roman architecture’s innovation. They present a double theatre with elliptical scene and a continuous grandstand. They were dedicated to fights between gladiators with beasts, or between them, and other similar mass spectacles.
They had hatches with systems to lift the beasts and flood mechanisms for naumachia (naval battles).
Example of how to organize a space for many people, masterpiece of logistics and deployment of personnel for its construction where they worked in several areas at the time.
The most known amphitheatre is the Colosseum in Rome.